Abstract
Objective
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis ( HLH) is a clinical syndrome which is caused by uncontrolled activation and proliferation of CD8+ T cell , and abundant releasing of in inflammatory cytokines. It has been confirmed that miR-146a is widely participate in the regulation of intensity of inflammatory response, while miR-30e is related to the regulation of NK cell cytotoxicity. In this study, RT-PCR was used to detect the expression of serum miR-146a and miR-30e in patients with secondary HLH (sHLH). Their correlation with clinical data, and diagnosis and prognosis value in sHLH patients were explored. In addition, their relation with the proportion of cytotoxic lymphocyte subsets and the expression of perforin were explored.
Methods
A total of 35 patients with sHLH and 10 healthy controls were enrolled in this study. Serum expression levels of miR-146a and miR-30e were detected by using RT-PCR. The expression of perforin protein oncytotoxic lymphocytes and the proportion of cytotoxic lymphocyte subsets were tested by flow cytometry. The clinical data of sHLH patients were collected.
Results
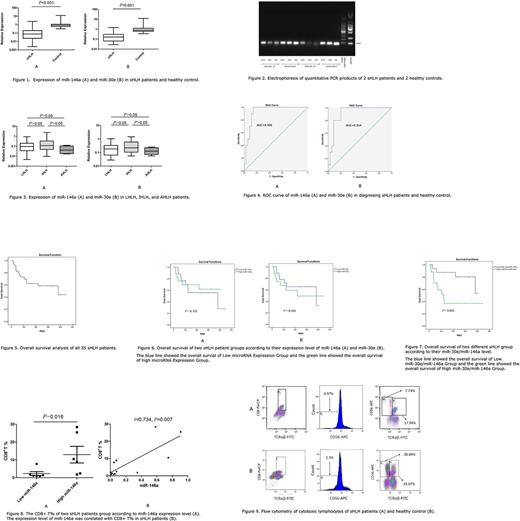
(1) The serum expression level of miR-146a in the newly diagnosed sHLH group was significantly lower than that of healthy control group (P <0.001); the serum expression level of miR-30e in the newly diagnosed sHLH group was significantly lower than that of healthy control group (P <0.001). (2) The serum expression level of miR-146a and miR-30e in the lymphoma-associated HLH group, the infection- associated HLH group, and the autoimmune-associated HLH group were compared group by group, however no significant difference was found (P >0.05). (3) ROC analysis revealed that the serum expression level of miR-146a can effectively identify sHLH patients from healthy people, with area under the curve (AUC) was 0.931; the serum expression level of miR-30e can effectively identify sHLH patients from healthy people, with area under the curve (AUC) was 0.914. (4) Correlation analysis was applied and no correlation was found between the serum expression level of miR-146a and miR-30e, and Age, WBC, HB, PLT, SF, ALB, ALT, AST, LDH, FIB, TG, ESR, sCD25, CRP level in the newly diagnosed sHLH (P >0.05). (5) According to the median of serum expression level, sHLH patients were divided in to Low expression group and High expression group. OS analysis was applied and revealed that there was no significance difference between the Low miR-146a expression group and the High miR-146a expression group (P >0.05); meanwhile there was no significance difference between the low miR-30e expression group and the high miR-30e expression group (P >0.05). However, sHLH patients were divided in to Low miR-30e/miR-146a group and High miR-30e/miR-146a group according to the median of miR-30e/miR-146a. The OS of Low miR-30e/miR-146a group was significantly longer than High miR-30e /miR-146a group (P=0.022). (6)The proportion of CD8+ T cell in Low miR-146a group was significantly lower than that in High miR-146a group (P = 0.016). The serum exression level of miR-146a was corelated with the proportion of CD8+ T cell (r=0.734, P = 0.007). However, the proportion of cytotoxic lymphocyte subsets in Low miR-146a group has no significant difference with that in Low miR-146a group (P >0.05); the serum exression level of miR-30e has no corelation with the proportion of cytotoxic lymphocyte subsets (P >0.05). (7) The expression of perforin in cytotoxic lymphocyte subsets in Low miR-30e group has no significant difference with that in Low miR-30e group (P >0.05); the serum exression level of miR-30e has no corelation with the expression of perforin in cytotoxic lymphocyte subsets (P >0.05).
Conclusion
The serum expression level of miR-146a and miR-30e in the newly diagnosed sHLH group was significantly decreased, which is important in the differential diagnosis of sHLH. Individuals with lower serum expression level of miR-146a and miR-30e were more likely to be sHLH patients. The ratio of miR-30e and miR-146a (miR-30e /miR-146a) can indicate the prognosis of sHLH patients. The prognosis of sHLH patients with lower miR-30e /miR-146a was better than that of sHLH patients with higher miR-30e /miR-146a. The serum exression level of miR-146a was corelated with the proportion of CD8+ T cell. The serum exression level of miR-146a was corelated with the proportion of CD8+ T cell. Therefore, miR-146a may play a role in the deficiency of CD8+ T cell in the pathogenesis of sHLH.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.